China xiaokang. com exclusive feature
Text | "Xiaokang" China Xiaokang.com reporter Liu Yanhua
According to the survey results of "China Modern Ecological Development Index 2023", fresh air and clean drinking water are the top eight elements of an ecologically livable city in the eyes of Chinese people.

Image source /hellorf
"What factors do you think a livable city should include in terms of ecological environment?" This is a topic in the questionnaire survey of "China Modern Ecological Development Index". The survey results of "2023 China Modern Ecological Development Index" show that "fresh air" ranks first among the eight elements of an ecologically livable city in the eyes of Chinese people, and nearly 90% of the respondents chose this option.
However, reality often makes people feel helpless. Because, the dust is coming again!
From May 18 to 20, a new round of sand blowing or floating dust was ushered in parts of eastern and southern Xinjiang, central and western Inner Mongolia, northern Gansu, northern Ningxia, northwestern Shaanxi, northwestern Shanxi and northwestern Hebei, and even sandstorms appeared in central Inner Mongolia. It is reported that at 16: 43 on May 18, a strong sandstorm occurred at Saiwusu Airport in Erenhot, Inner Mongolia, with an instantaneous wind speed of 27 m/s and visibility of only 150 m. The rolling yellow sand was like a giant "sand wall".
According to the three major action plans for air pollution control, the goal of basically eliminating heavy pollution days nationwide in 2025 is to control it within 1%, including eliminating such dusty weather. Dust is a common meteorological disaster. Because of the existence of natural desert, sandstorm, as a natural process and phenomenon, is difficult to be eliminated, but desertification land management can effectively reduce the frequency and intensity of sandstorm. Since the beginning of this century, China has implemented a series of ecological restoration projects. The results of the sixth national survey on desertification and desertification show that for the first time, China has achieved a "double reversal" of desertification and desertified land in all provinces surveyed, with a continuous "double reduction" in area and a continuous "double reduction" in degree, and a continuous "double improvement" in vegetation coverage and carbon sequestration capacity of deserts and sandy land. However, desertification control in China still has a long way to go. As of 2019, the area of desertification land in China is 2,573,700 square kilometers, accounting for 26.81% of the country’s land area; Desertification land covers an area of 1,687,800 square kilometers, accounting for 17.58% of the national territory; The land area with obvious desertification trend is 279,200 square kilometers, accounting for 2.91% of the national territory. According to official data, the cumulative number of dust storms from January to May is 11.9 times all the year round, but it is obviously higher this year, reaching 14 times as of May 20th.
The frequent occurrence of dust and sand once again sounded the alarm of ecological security for people.
Compared with air quality, water pollution is more worrying.
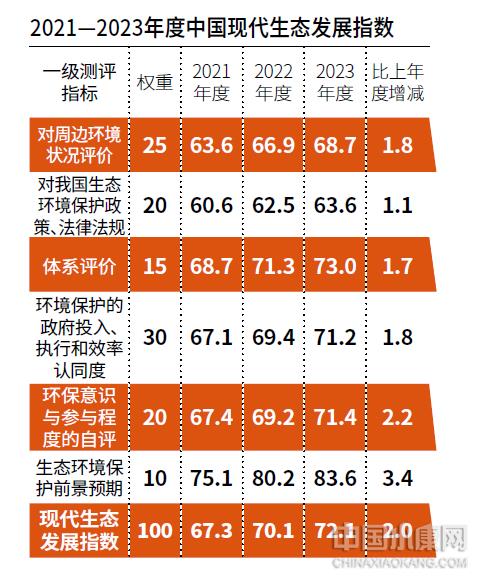
From April to May, 2023, Xiaokang magazine, in conjunction with the National Information Center, and together with relevant experts and institutions, conducted a survey on "2023 China Modern Ecological Development Index". "China Modern Ecological Development Index" was born out of "China Ecological Well-off Index", followed the objective situation and development trend of the times, and was updated and perfected. It was mainly measured from five aspects: the public’s evaluation of the surrounding environment, the evaluation of China’s ecological environmental protection policies, laws and regulations, the recognition of government investment, implementation and efficiency in environmental protection, the self-evaluation of environmental awareness and participation, and the expectation of ecological environmental protection prospects.
After weighting the survey results and the statistical monitoring data of relevant state departments, it is concluded that the modern ecological development index of China in 2023 is 72.1 points, 2.0 points higher than the previous year. Among them, the evaluation of the surrounding environment, the evaluation of China’s eco-environmental protection policies, laws and regulations, the recognition of government investment, implementation and efficiency in environmental protection, and the self-evaluation of environmental awareness and participation are 68.7 points, 73.0 points, 71.2 points, 71.4 points and 83.6 points, respectively, which are 1.8 points, 1.7 points, 1.8 points and 83.6 points higher than the previous year.
Strengthening the prevention and control of air pollution is the common aspiration of the whole society. With the implementation of the Air Pollution Prevention Action Plan and the Three-year Action Plan to Win the Blue Sky Defence War, China’s air quality has been greatly improved since 2013. In the past ten years, China’s GDP has increased by 69%, the concentration of PM2.5 has decreased by 57%, achieving ten consecutive declines, the number of days of heavy pollution has decreased by 92%, and the concentration of sulfur dioxide has dropped to single digits; The national emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides dropped from more than 20 million tons to about 3 million tons and 9 million tons, respectively, down by 85% and 60%.
However, as Liu Bingjiang, director of the Atmospheric Environment Department of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, said at the regular press conference held by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment in March, "the improvement effect is still not stable." Especially this year, with the comprehensive recovery of economic and social activities, the increase of emissions, and the impact of climate change, the air quality situation is not optimistic. Not only have there been 14 rounds of large-scale dusty weather, but ozone pollution has also appeared in Jinan and Zhengzhou.
This is also reflected in the "2023 China Modern Ecological Development Index" survey. Facing "What do you think of the air quality in your city?" On this issue, 51.4% of the respondents thought it was "relatively good" and 12.5% of the respondents bluntly said it was "very good", making a total of 63.9%, a decrease of 0.1 percentage point over the previous year. Respondents who thought it was "relatively poor" accounted for 10.8%, and those who bluntly said it was "very poor" accounted for 1.4%, making a total of 12.2%, a decrease of 2.0 percentage points over the previous year. In addition, 23.9% of the respondents rated it as "average", an increase of 2.1 percentage points over the previous year.
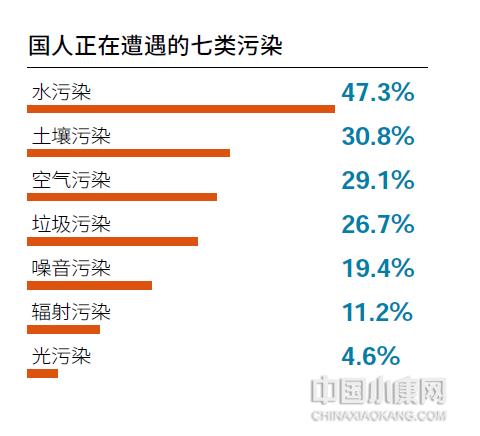
However, water pollution and soil pollution are more worrying than air pollution. In this year’s "List of Pollution Types that Seriously Threaten the Public", "Water Pollution" topped the list, and 47.3% of the respondents said that they were being threatened by water pollution. "Soil pollution" surpassed "air pollution" for the first time, ranking second, with a vote rate of 30.8%.
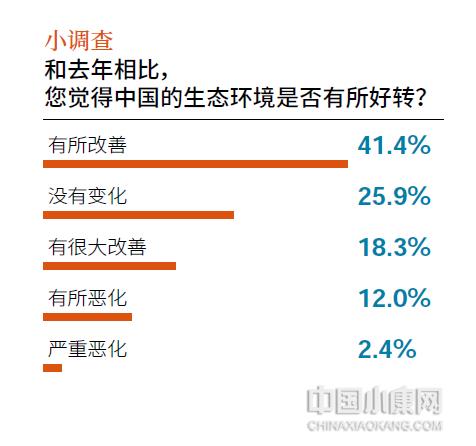
Water is the source of life and the starting point of ecological civilization construction. The survey results of "2023 China Modern Ecological Development Index" show that 59.3% of the respondents rated the water quality of daily water (tap water, accumulated water, etc.) as "average", 13.4% as "poor", 2.6% as "very poor", and only 24.7% of the respondents gave a positive evaluation, less than a quarter. However, the evaluation of the natural water bodies (streams, rivers, lakes and seas) in the city is not optimistic, with less than 20% respondents giving positive comments, 26.5% respondents thinking that they are "poor" and "very poor", and 54.7% respondents evaluating them as "average".
In fact, in the first half of this year, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment also said in response to a reporter’s question that China’s water ecological environment protection has undergone a major turning point, but the structural, root and trend pressures faced by water ecological environment protection have not been fundamentally alleviated, the imbalance and uncoordinated improvement of water environmental quality is prominent, the ecological water supply for rivers and lakes is insufficient, the water ecological damage is prominent, and the water ecological environment risk is still high, which is still far from the requirements of beautiful China construction.
Seven difficult problems of environmental governance, strengthening supervision and consolidating responsibility
Continuing the convention, the "2023 China Modern Ecological Development Index" survey asked the respondents to select seven difficult problems in China’s environmental governance work again. The first one is "enterprises only care about their own economic interests and lack social responsibility" (36.0%), the second one is "local governments are driven by interests and lack of implementation" (31.3%), and the third one is "public environmental awareness is insufficient". The fourth to seventh places are "China’s industrial structure is unreasonable, and the proportion of heavy industrial enterprises with high energy consumption is too large" (24.6%), "lack of relevant laws and regulations" (21.9%), "the development idea of" pollution first, then treatment "still exists" (18.3%) and "limited power of environmental protection departments" (5.2%).
It can be seen that it is still an important task for China to realize the modernization of national governance system and governance capacity to accelerate the construction of a modern environmental governance system with the leadership of party committees, government-led, enterprise subjects, social organizations and the public participating together.
At the end of 2022 and the beginning of 2023, an 11-day New Year’s haze occurred in China, concentrated in Shaanxi and Henan. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment launched an emergency plan for heavy pollution, but the effect was not satisfactory. In order to find out, Huang Runqiu, Minister of Ecology and Environment, and Zhao Yingmin, Vice Minister of Ecology and Environment, went to 13 enterprises in Henan and Shaanxi to carry out inspections in the way of "four noes and two straights" from February 20 to 22, and found that there were a lot of outstanding environmental violations such as abnormal operation of pollution control facilities, illegal discharge, fraudulent production accounts, online monitoring and manual monitoring.
Frequent corporate environmental violations have fully exposed the shortcomings and weaknesses in China’s current environmental governance. First, some enterprises ignore the law and break through the bottom line. Second, in some places, the determination to tackle pollution is insufficient and the tenacity is insufficient. Third, the ecological environment supervision in some places is superficial and weak.
Only by implementing the strictest system and the strictest rule of law can we provide a reliable guarantee for the construction of ecological civilization. A few days ago, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment completed the revision of the original Measures for Environmental Administrative Punishment, and issued the newly revised Measures for Ecological Environmental Administrative Punishment, making adjustments in the types of punishment, time limit, authority, procedures and law enforcement methods, responding to new changes in the reform process and new problems that need to be solved urgently in local areas, and ensuring that the law enforcement team of ecological environment strictly regulates and carries out law enforcement activities according to law.
In addition, the red line system of ecological protection is an important institutional innovation of ecological environmental protection in China, which provides a brand-new ecological protection model. The latest news shows that at present, the national ecological protection red line has been delineated and released. The following question is how to protect, use and implement the red line of ecological protection.
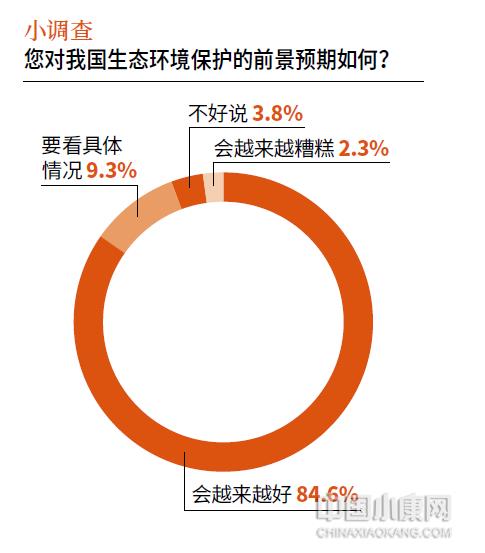
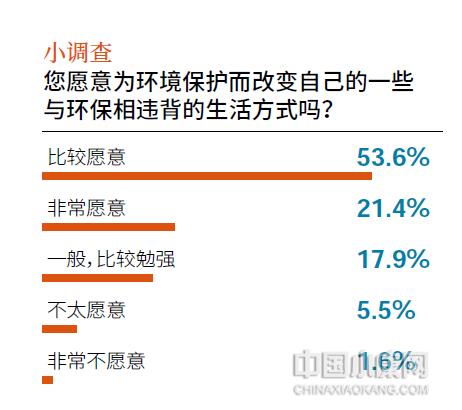
Keeping the red line of ecological protection and building an ecological security barrier need to be implemented steadily from multiple angles, and arousing public awareness of environmental protection is one of the important tasks. The survey of "2023 China Modern Ecological Development Index" shows that the public’s awareness of environmental protection needs to be further improved, and 75% of the respondents are willing to change their lifestyles that are contrary to environmental protection for environmental protection, which is 11.9 percentage points lower than the previous year.
("Xiaokang" China Xiaokang. com exclusive feature)
This article was published in the June 2023 issue of Xiaokang.