Text/degree
Huawei’s mobile phone was forced to withdraw from the high-end market because the supply of 5G chips was clamped down by the United States. In the past two years, domestic mobile phone manufacturers have hit the high-end market in succession, trying to occupy the market share given up by Huawei. Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, and glory have piled up hardware, played joint names, and made great efforts in marketing.
A common feature is that mobile phone manufacturers have generally launched sub-brands that take the cost-effective route (such as Xiaomi’s sub-brand Redmi, OPPO’s sub-brand realme, and vivo’s sub-brand iQOO), while parent brand has turned its course to the high-end market.
But this trend was quickly attacked by Apple. The strong momentum of iPhone13 series has given a heavy hammer to domestic mobile phones.
Data show that after the release of the iPhone13 series, Apple ranked first in the smartphone market in China in October 2021, which is the first time that it has returned to the first place in China since December 2015. In November 2021, Apple continued to be the first in the China market, with a market share of 23.6%.
In addition, Apple overtook Xiaomi in the third quarter of 2021 and regained the second place in global sales. Affected by the boost of new product sales, Apple’s total market value once exceeded $3 trillion in the early morning of January 4, 2022, becoming the first company in the world to enter the $3 trillion club.
"Xiaomi’s market share declined in the third quarter (2021), mainly related to the strong performance of iPhone13." Wang Xiang, president of Xiaomi Group, said so on the performance conference call in the third quarter of 2021.
As we all know, Apple’s iPhone has taken three-quarters of the profits of the global mobile phone industry. Only by taking the mid-to-high-end iPhone (the cheapest mobile phone sold by Apple in official website is the iPhone SE, with a price of 3,299), Apple can become the second largest seller in the world, which shows its unshakable position in the high-end market.
On the other hand, domestic manufacturers, after Huawei, have no one to stop Apple’s offensive in the high-end market. An outstanding performance is that after the release of the iPhone13 series in 2021, the price of domestic mobile phones began to "dive" wildly in a second-hand market.
The reason is that with the escalating arms race of mobile phone hardware, it is increasingly difficult for domestic mobile phone manufacturers who lack autonomy in hardware and whose core supply chain is controlled by others to break through in product strength.
If the core supply chain problem is not solved, domestic mobile phone manufacturers will only become more and more passive in the next generation of computing equipment with more extreme performance requirements represented by AR/VR.
01 Apple’s "open plan"
In double 11 in 2021, the price of flagship machine Xiaomi Mix 4 just released by Xiaomi in August plunged sharply into 1000 yuan, and the starting price dropped from 4,999 yuan to 3,999 yuan. The news of price reduction once rushed to the second place in Zhihu’s digital hot list.
In this regard, many users who bought Mix 4 for the first time poured bitterness on social networking sites: "double 11 directly dropped 1,000 yuan. Who will buy the starter in the future? Is the high-end positioning so branded?" "Lei Jun said that Xiaomi only earned 5% of the profits. I believe it. Is it a loss to sell the price down by 1,000 yuan?"
In fact, it has been the norm for many years that the value of Android phones is low and the price "diving" after a period of sale. However, in 2021, the price reduction of flagship machine, a domestic manufacturer, was particularly prominent.
For example, the price of one plus nine Pro double 11 with a starting price of 4,999 yuan dropped to 3,799 yuan, and the price of vivo flagship machine X60 Pro+ double 11 with a starting price of 4,998 yuan dropped to 3,999 yuan, which made many old users call it "broken defense".
Faster price cuts and lower prices naturally mean the loss of profit margins for mobile phone manufacturers, but even so, the price cuts made in flagship machine have not brought about a significant improvement in sales.
According to the report released by BCI, a market research organization, during the two weeks (10.25-11.7) of the Double Eleven intensive promotion, Apple’s sales in the domestic market were far ahead.
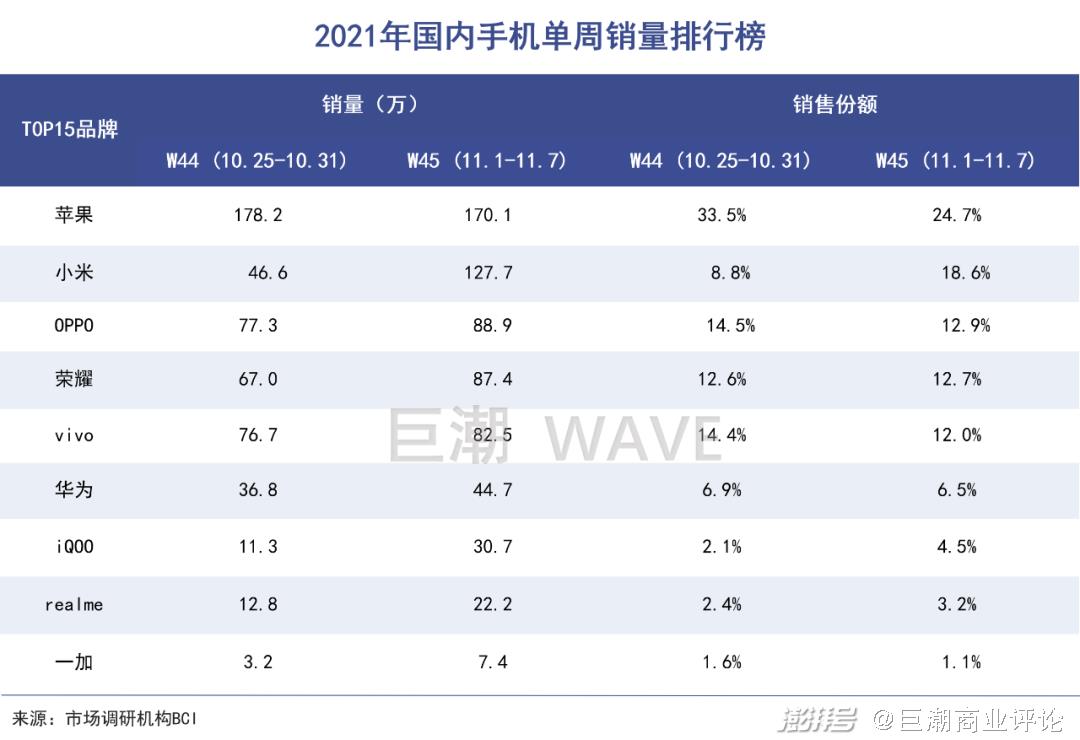
The reason is that this is not unrelated to Apple’s initiative to cut prices on the iPhone13 series. This year’s iPhone13 series has been added and reduced in price, and the sales of its products are obvious to all. The 13 Pro series with high version is continuously out of stock.
It is reported that the official price of the 64GB version of the iPhone 12 released in 2020 is 6299 yuan, while the official price of the 128GB version of the iPhone 13 released in 2021 is only 5999 yuan. In addition, various e-commerce activities in double 11 give subsidies ranging from 200 to 500, which makes many netizens shout: Thirteen Fragrances!
Some people in the mobile phone industry believe that the price reduction of the iPhone 13 series is Apple’s "open plan". Apple took the initiative to attack, trying to disrupt the strategic pace of domestic manufacturers attacking high-end, and stop the emergence of "the next Huawei".
From the perspective of the sales volume of domestic mobile phone manufacturers and the "diving" of flagship model prices, Apple’s "open plan" is very effective. In the domestic high-end market, it is difficult for domestic manufacturers to match it.
02 technical short board exposure
Apple is not always a Ma Pingchuan in the high-end market, and it is difficult to meet its rivals. In 2020, Huawei’s mobile phone reached its peak, and it was even with Apple in the high-end market.
According to IDC’s data, in the first half of 2020, Huawei and Apple accounted for nearly 90% of the domestic mobile phone market share in the price range of more than $600, reaching 88.1%. Huawei ranked first ahead of Apple by 0.1%.
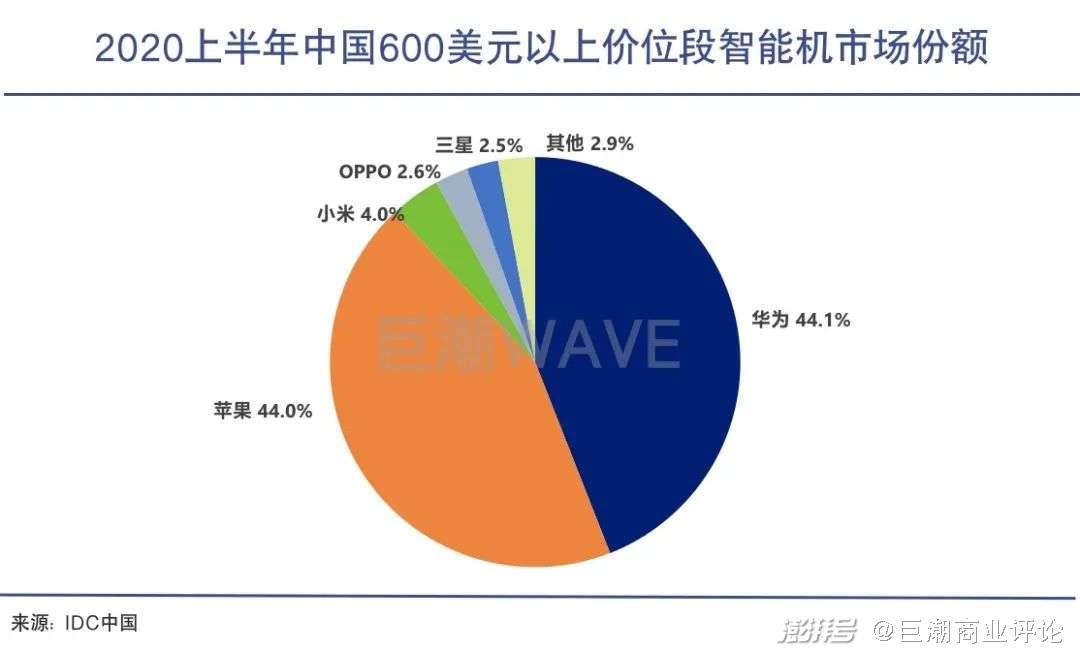
But unfortunately, since Huawei’s mobile phone "fell" from the peak because of the chip being suppressed, it is difficult for domestic manufacturers to succeed Huawei and compete with Apple.
This is not unrelated to the technical shortcomings of domestic mobile phone manufacturers.
In the core components such as screen, core processor, CMOS image sensor, especially SoC chip, domestic mobile phone factories such as Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo and Glory all rely on the support of supply chain, while Apple, Samsung and Huawei have all achieved partial autonomy and self-research. It is for this reason that domestic mobile phone manufacturers (except Huawei) have been criticized as "advanced assembly plants".
Especially the SoC of mobile phones, in this field, Huawei used to rely on the Kirin 9000 chip developed by itself to achieve the same performance as Apple A14 chip. However, with the suppression of high-end chips, the self-developed SoC chips have become a swan song, and the high-end flagships of Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, Glory and other manufacturers all adopt the outsourced Qualcomm Snapdragon SoC chips.
In 2021, when the fever problem of Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 became "Fire Dragon 888", it was difficult for Android phones to compete with Apple using A15 processor in terms of performance and power consumption, and the problem of supply chain autonomy was exposed.
Specifically, the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 chip in 2021 has some problems, such as high power consumption, high calorific value and fast battery consumption, which greatly reduces the experience of domestic high-end mobile phones in 2021.
The mobile phone manufacturer most negatively affected by "Dragon 888" is Xiaomi. Since the release of Xiaomi 11 series, users have constantly reported that Xiaomi 11 series has serious problems of fever, motherboard burning and WiFi burning. The incident has also been reported by many media.
Even so, the flagship models of domestic mobile phone manufacturers are still dependent on Qualcomm. Qualcomm is almost dominant in the field of high-end SoC of mobile phones.
Just recently, Xiaomi and Lenovo, two domestic mobile phone manufacturers, fought a small "battle" over "who will launch Qualcomm Snapdragon’s next-generation SoC", and Lenovo’s Motorola brand finally won the top spot.
However, it is worth pondering that the performance of Qualcomm’s new generation SoC Snapdragon 8 Gen1 in terms of power consumption and heat generation has not improved much compared with the previous generation 888. A number of commentators pointed out that the mobile phones equipped with Snapdragon 8 Gen1 currently on the market generally adopt the methods of frequency reduction, frame locking and resolution reduction to control the fever of the mobile phones, which makes a certain discount on the actual experience.
Self-developed chip: a difficult and correct way
In fact, Snapdragon 888 chip is not the first time that domestic mobile phone manufacturers have suffered from Qualcomm. In 2015, Qualcomm Xiaolong 810 chip was once called "fire dragon" because of its high power consumption and fever, which dragged down the product strength of a number of Android flagship mobile phones.
In the case that the core supply chain is controlled by people, once an accident happens, it is difficult for mobile phone manufacturers to avoid the negative impact, and there is great uncertainty behind it.
Perhaps affected by this, domestic mobile phone manufacturers have long developed the idea of self-developed mobile phone SoC. Unfortunately, except Huawei, domestic mobile phone manufacturers have not successfully got rid of their dependence on Qualcomm’s flagship chip.
In 2017, the Xiaomi 5C mobile phone released by Xiaomi was equipped with a self-developed 澎湃 S1 processor, but the subsequent 澎湃 S2 failed several times, and the core-making plan finally ran aground.
It is reported that ZEKU (Zheku Technology), a chip subsidiary of OPPO, is also developing SoC chips. Some media pointed out that OPPO plans to OEM its 3 nm SoC chip developed by TSMC. If the research and development is successful, it will be carried on the flagship mobile phone launched in 2023 or 2024.
Judging from the failure experience of Xiaomi 澎湃 S2 and Huawei’s exploration, it is very difficult to develop a mobile phone SoC chip. It takes at least three years to develop a SoC chip, and a lot of money is invested. Lei Jun once described core-building as "a narrow escape" in a speech. This is a great test for the financial resources and courage of mobile phone manufacturers.
However, it is more meaningful to persist in the difficult and correct things. Self-developed SoC can help mobile phone manufacturers to better control the integration of software and hardware, and widen the gap with competitors in experience, especially in the case that Qualcomm’s flagship processor products are not strong enough.
From a longer-term perspective, the next generation of computing platforms, whether AR, VR or Metauniverse, will have significantly higher requirements for software and hardware than mobile phones. This also puts forward higher requirements for the performance of smart device SoC.
Especially the metauniverse, Intel Company pointed out that the metauniverse may be the next major computing platform after the World Wide Web and mobile phones, but the current computing, storage and network infrastructure is simply not enough to realize this vision, and the collective computing power of human beings needs to be improved at least 1000 times.
This means that the next generation of computing platforms will have more extreme requirements for the performance of terminal equipment, and enterprises with self-research capability of SoC chips and high integration of software and hardware will be the winners in the future.
04 written at the end
In terms of software and hardware integration, Apple, which has a closed IOS ecosystem and super A series chips, is second to none. Developing Android system Google also equipped a self-developed Tensor processor on the latest Pixel 6 series mobile phones, trying to make up for the shortcomings on the SoC chip.
However, domestic mobile phone manufacturers still rely more on Android system in software level, and lack the design and manufacturing ability of SoC in hardware level. If this situation is not effectively improved, the road for domestic mobile phone manufacturers will be more and more narrow in the competition of the next generation computing platform.
The core chip is controlled by people, and it is difficult for domestic mobile phones to break the high-end situation of Apple’s "hegemony". The phenomenon that Apple takes three-quarters of the profits of the whole industry will continue to be staged.